Overview of Attribution Models
- What are Attribution Models?
- Why are Attribution Models Important?
- What are the Types of Attribution Models?
- Which attribution model should I choose?
- Quick Overview: Position-Based vs. Data-Driven Models
- Position-Based Attribution Models
- Data-Driven Models
- Video Guide: What’s the best attribution model for B2B marketers?
- Applying Attribution Models to your reports
- FAQ
In this article, we will walk you through an overview of Attribution Models. We will cover:
- What these models are and why they are important.
- The specific types of Attribution Models that DreamData provides.
- How to choose the Attribution Models for your needs.
What are Attribution Models?
Attribution models are frameworks used in digital marketing and analytics to assign credit to various touchpoints or interactions in a customer’s journey toward a conversion or sale. These models help companies understand which channels, campaigns, or interactions are most effective in driving desired outcomes, such as sales, sign-ups, or other conversions.
Why are Attribution Models Important?
Attribution models help businesses:
- Optimize marketing budgets: By understanding which channels are most effective, marketers can allocate resources to the highest-performing tactics.
- Enhance campaign strategies: Insights from attribution models reveal which customer interactions contribute to conversions, allowing for more targeted and effective marketing strategies.
- Improve ROI: With a clearer understanding of what drives conversions, businesses can focus on tactics that deliver the best return on investment.
What are the Types of Attribution Models?
Dreamdata provides you with 6 attribution models: First-touch, Last-touch, Linear, W-shaped, U-shaped, and Data-Driven attribution models. Each attribution model distributes a certain percentage of credit for a conversion across each touchpoint differently.
Within Dreamdata, you can switch between these models to compare their value distribution. This comparison helps you understand which touchpoints to prioritize in your customer journey, as the amount of credit per touchpoint varies depending on the model used. By analyzing each model, you can gain a better perspective on the ROI for specific channels or paid ads.
Which attribution model should I choose?
There is no single solution that fits every scenario. The right choice depends entirely on what you wish to measure and analyze. It is important to distinguish between the two main categories: Position-Based models and Data-Driven models.
Quick Overview: Position-Based vs. Data-Driven Models
Position-Based Models, also known as rule-based models, assign credit using heuristic business rules. These are typically tied to where the touchpoint occurs in the customer journey. These models analyze a single journey at a time and adhere to a fixed, pre-defined set of rules. This category includes the First-touch, Last-touch, Linear, W-Shaped, and U-Shaped models.
Data-Driven Models define their own rules by analyzing all your customer journeys simultaneously. You should use Data-Driven attribution if you want to attribute weight based on how touchpoints historically influence successful outcomes, rather than relying on a fixed position in the funnel.
Position-Based Attribution Models
Position-based attribution models rely on a set of rules to determine how value is assigned to different touches. Each touch is assigned a specific percentage of credit, usually depending on when it occurred in the journey.
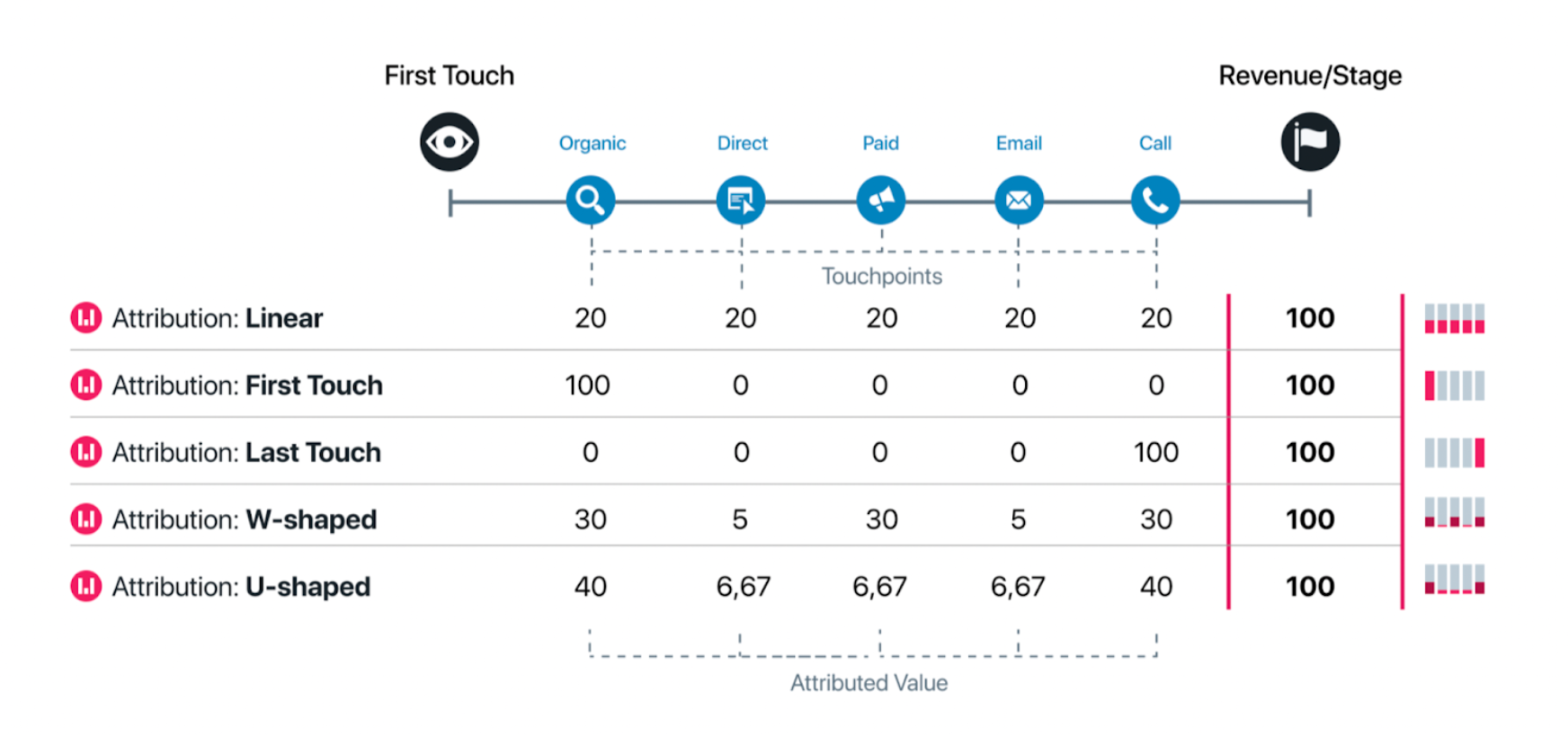
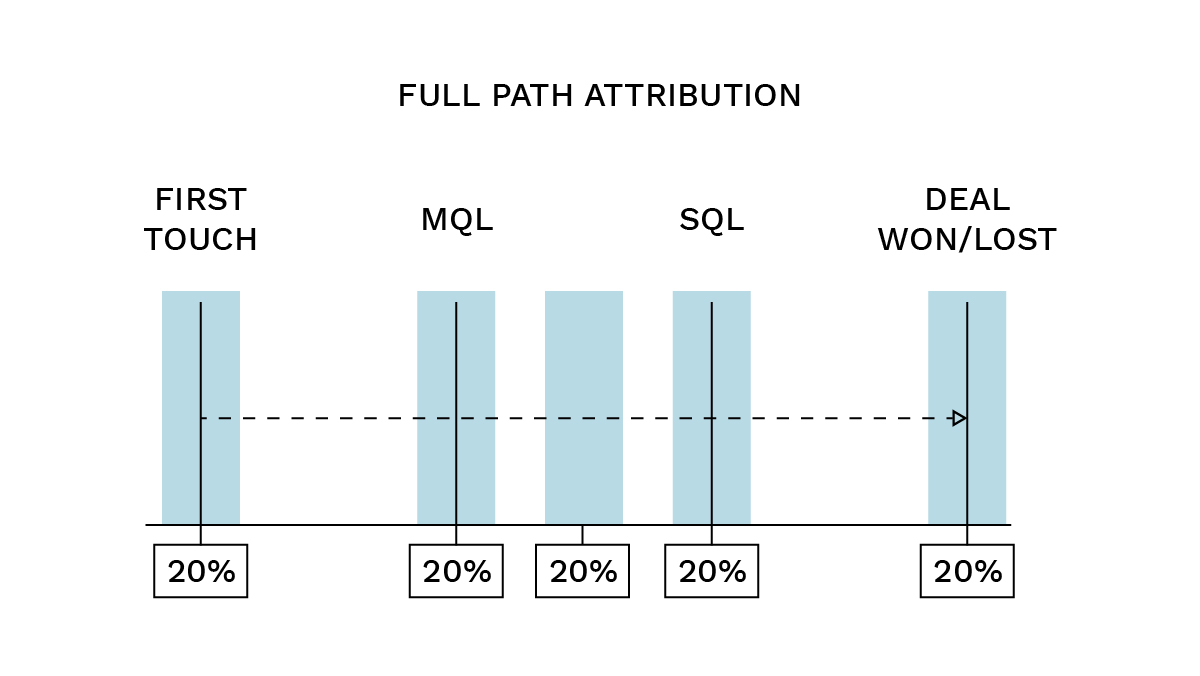
- Linear: Every touch is assigned an equal amount of credit. For example, if there are five touchpoints, each receives 20% of the credit. This model works well when all touchpoints leading up to a stage conversion are considered equally important.
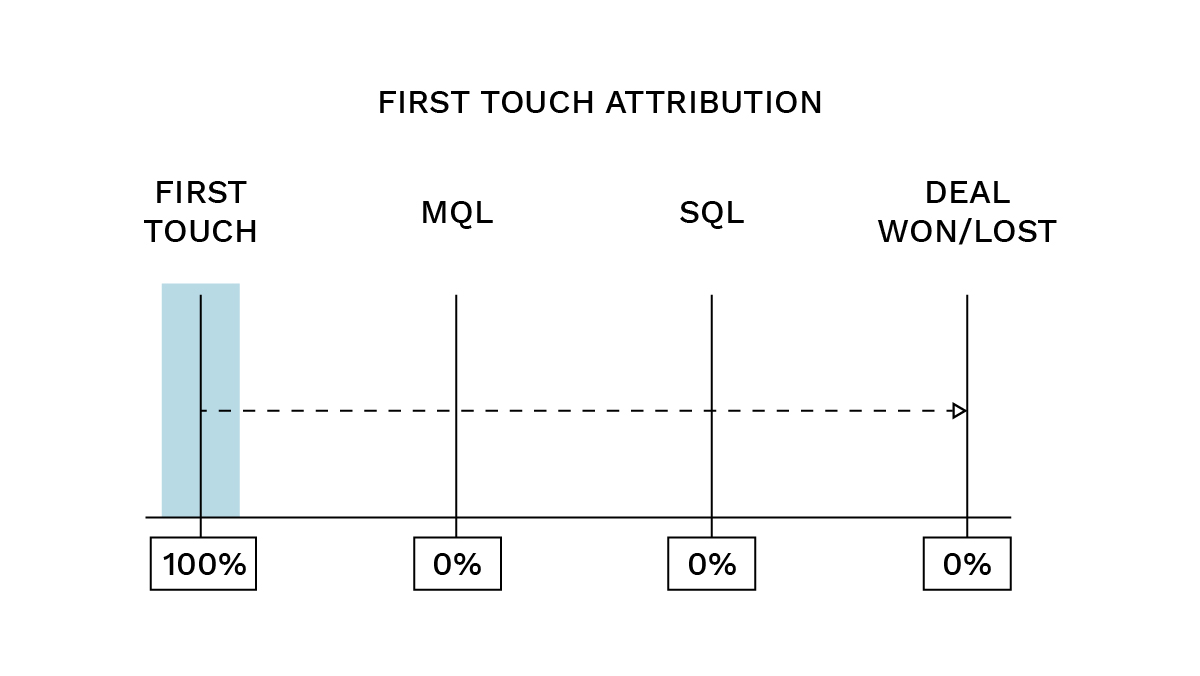
- First-touch: The very first touchpoint receives 100% of the credit. This model is ideal for short sales cycles, clear customer journeys, or when a company wants to emphasize brand awareness and the earliest touchpoints that drive initial interest, such as an MQL.
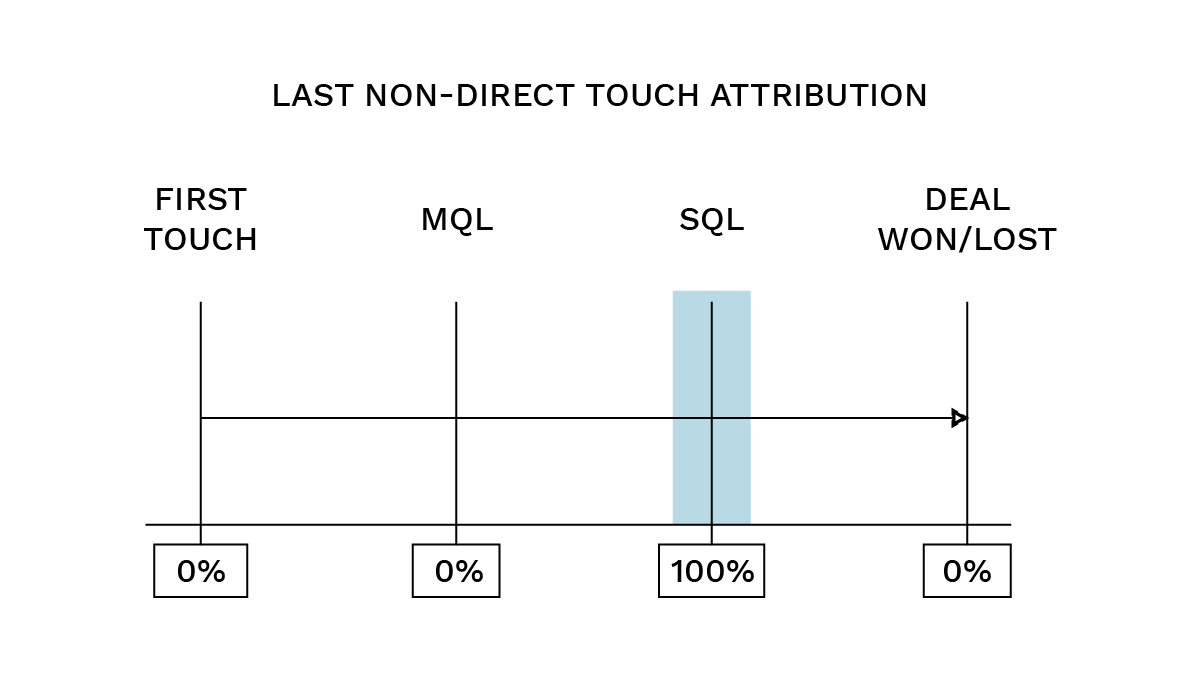
- Last-touch: The very last touchpoint receives 100% of the credit. Similar to First-touch, this works well for short sales cycles and clear journeys, but it is best used when a company wants to emphasize the final interaction that occurred immediately before a stage conversion.
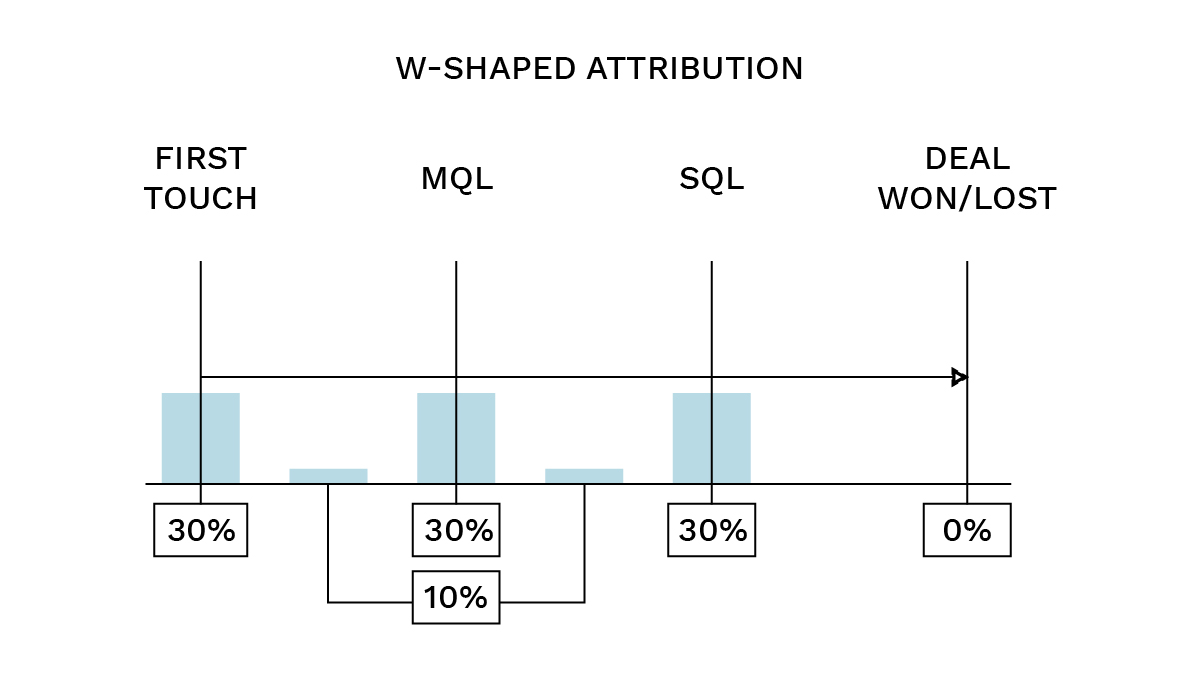
- W-shaped: This model distributes credit heavily to the key milestones. 30% of the credit is given to the first touch, 30% to the last touch, and 30% to the touch containing the conversion. The remaining 10% is divided among the middle touches. This multi-touch model is excellent for complex customer journeys where the entry, exit, and conversion points are the most critical, while still acknowledging the supporting interactions.
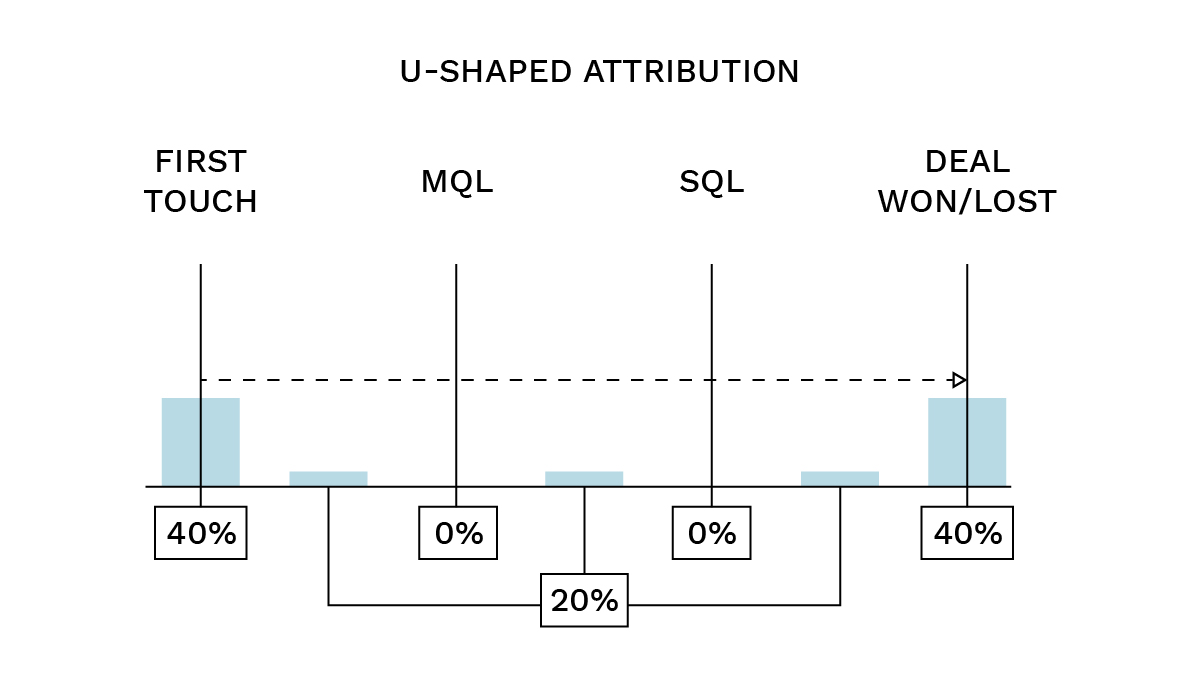
- U-shaped: Here, 40% of the credit is given to the first touch and 40% to the last touch. The remaining 20% is divided among the remaining middle touches. This is useful for complex multi-touch journeys where the introduction and the conclusion are of the highest importance, with less weight attributed to the nurturing steps in between.
You may for example choose the W-Shaped model as your primary attribution model for reporting and analysis. This is a good option as it does not distribute the credit equally amongst all the touch points, but highlights the ones with more importance, as well as includes those that have little impact but contribute to the journey.
Generally speaking, you don't need to limit yourself to one attribution model and stick with it. It is recommended to compare performance under each model to understand the importance of multiple touch points in the customer's journey.
Data-Driven Models
Data-Driven Models replace specific business rules with a mathematical algorithm. This algorithm uses data from all your journeys to dynamically determine which touchpoints influenced a given stage and should therefore receive credit.
The main benefit of position-based attribution models is their explainability. You can look at a single journey, follow the rules, and clearly understand the score. In contrast, Data-Driven models consider all journeys at the same time. This allows the model to identify patterns across your entire data set, but it comes at the cost of transparency. You can no longer fully explain the attribution by looking at a single customer journey in isolation.
Video Guide: What’s the best attribution model for B2B marketers?
In this video, we cover several key topics regarding attribution strategy:
- The Prerequisites for Attribution: We explain why you must consolidate siloed data into a unified Account-Based timeline and how to handle B2B journeys involving multiple stakeholders.
- Defining Your Scope: How to select the specific pipeline stage for analysis, such as measuring from First Touch to MQL.
- Real-World Application: A marketer's perspective on using the First Touch model to measure top-of-funnel impact and justify spend on channels like LinkedIn Ads.
Applying Attribution Models to your reports
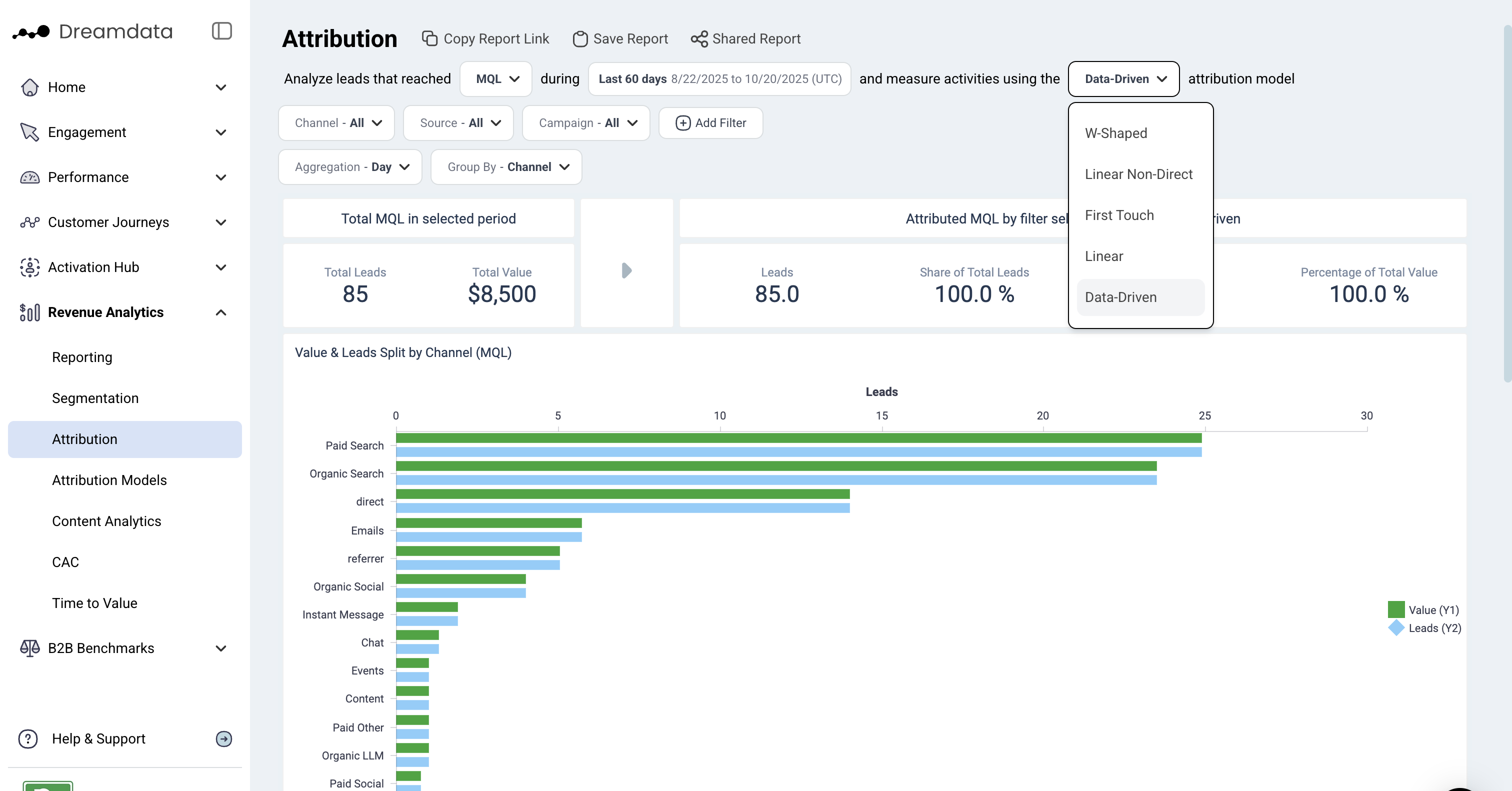
To toggle between the different attribution models, click the attribution model filter located at the top of the page. As you switch between different models, you will notice that the value attributed across your different channels and sources changes to reflect the new logic.
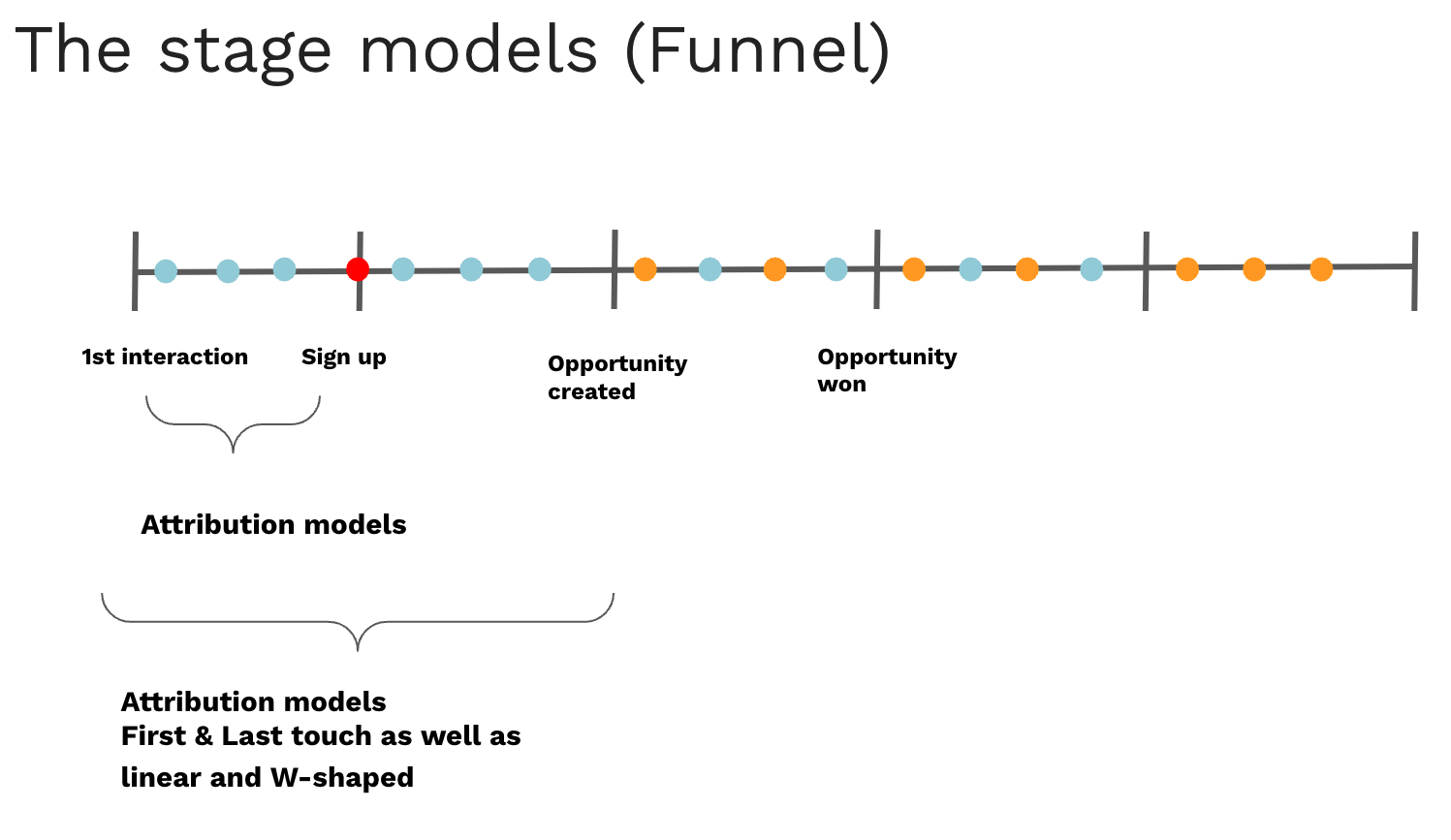
Attribution models can be applied from the first interaction to the first stage of your sales funnel or across your entire funnel. It is important to remember that the system always analyzes the touchpoints that occurred before a lead reached a specific stage. We will always calculate the value from the first interaction up to the stage you selected. In our example below, that would be all the blue dots before the red one, which is when a person "signs up" for something. We will always count from the first interaction to the stage you selected.
FAQ
Is it possible to customize an attribution model?
Yes, it is possible to customize your attribution models with Attribution Exclusions.
On enterprise plans, you have the opportunity to create completely custom attribution models where you can define complex business rules that divide credit based on any combination of event, campaign, channel, source, or position in the customer journey.
If you require fully customized Attribution Models, please get in touch with your Dreamdata Customer Success Manager. We can help ensure you select the best option before investing time and resources.

